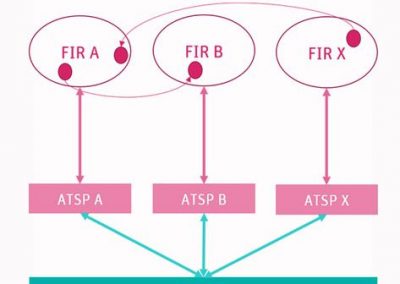
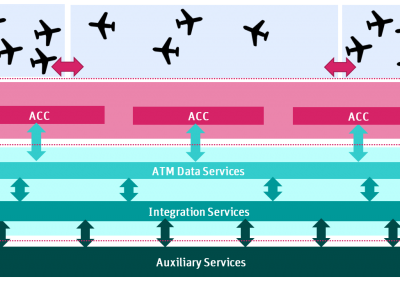
The Airspace Architecture Study (AAS) proposed a transition to a distributed architecture that leverages the latest digital technologies to enable significant performance increases in the European Air Traffic Management (ATM) system. This transformation focuses on technologies that allow the virtualisation of its infrastructure and air traffic service provision. The architecture proposed by the AAS is based on three operational layers including the notion of a new form of service provider – the ATM Data Services Provider (ADSP) – which would enable certain services currently provided within an area control centre to be provided remotely.
However, a successful transition requires service providers to invest in these new technologies and to adopt operational concepts and business models.
Project RoMiAD (Role of Markets in AAS Deployment)
Project RoMiAD, a catalyst project of SESAR’s Engage Knowledge Transfer Network (KTN), considered how cost efficiency in en-route Air Traffic Management (ATM) can be increased through adoption of the AAS architecture and how the necessary transition can be incentivised. To do so, the impact of various benefit mechanisms in the 2019 cost base and the application of various market instruments have been explored.
Paul Ravenhill and Maribel Tomás, authors of RoMiAD, have created various resource material and participated in various workshops which are highlighted below:
White Papers & Reports
Blogs & Media
External References
At Think, we have co-authored and contributed with our thinking to a number of virtualisation documents that lead the topic. A selection of these can be found below:
-
- Airspace Architecture Study
- CANSO – Emerging technologies for future skies: Virtualisation
- EUROCAE WG-122 Virtual Centre Standardisation (Soon to be published)



Project RoMiAD has received funding from the SESAR Joint Undertaking under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 783287. The opinions expressed herein reflect the authors’ view only. Under no circumstances shall the SESAR Joint Undertaking be responsible for any use that may be made of the information contained herein.







Recent Comments